Rescale Cloud Computing Performance Benchmarks
Table of contents
Mixing Tank
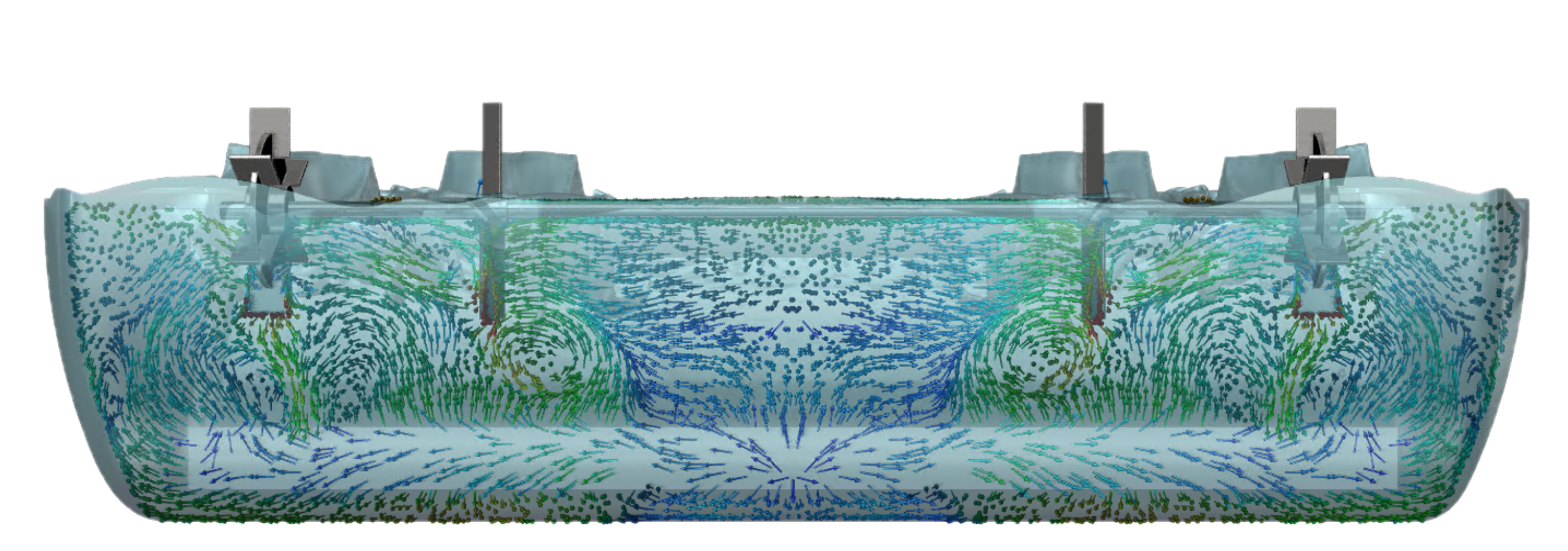

The Case
A steady-state, 3D and two-phase Volume of Fluid (VOF) mixing tank simulation was used to evaluate solution times across different hardwares. The benchmark test involved two personal workstations and five different core configurations in Rescale cloud, which utilized CloudConnect for job submissions to Rescale.
The case has approximately 4.7 million poly-hexcore cells, featuring a symmetry boundary in the middle. Impeller movement was modelled with Moving Reference Frame (MRF). A pressure-based coupled solver with the k-omega viscous model was used to run 2000 iterations. Energy equations was left out.
The table below displays the results. Total time refers to the duration from clicking calculate to until when the results are obtained. For Rescale jobs, the total time encompasses the time it takes to upload files to Rescale, start and stop the cluster, and download files to your local machine.
The time taken for sending jobs to Rescale and receiving results back on the local workstation was consistent across all test cases. The process of writing, preparing, and uploading files (case, data, journal and command) to Rescale, create the job and start the calculation took 1 minute. Downloading the case and data files and reading them took 3 minutes. The workstation employed for this task was a Lenovo laptop. The Rescale Command Line Interface (CLI) was used and the network upload/download speed was 20 MB/s.
In an additional test, the same case was simulated using a poly-hexcore mesh containing 18.3 million cells. Identical settings and geometry were maintained. This time 1000 iterations were solved.
Results
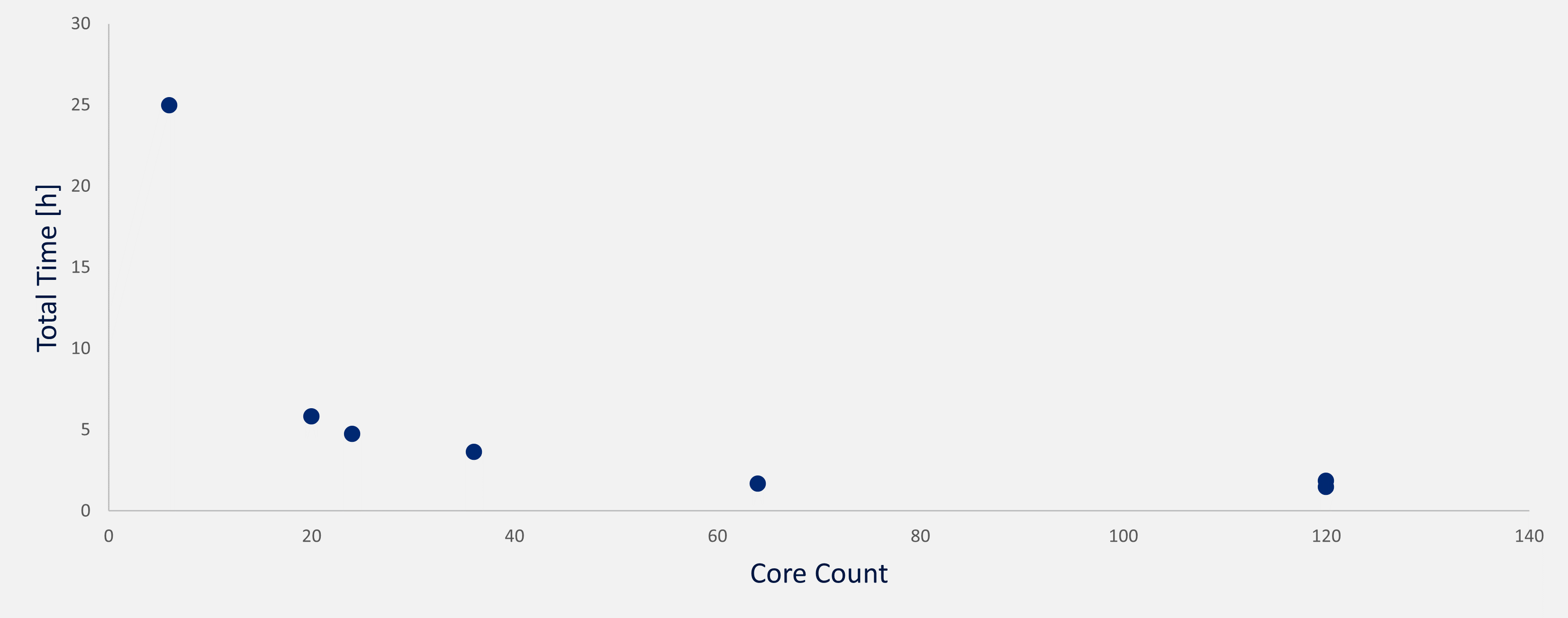
4.7 million cells
| Core Count | Processor | System memory | Run time | Total time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workstation - Lenovo P15v | 6 | Intel i7-10850H @ 2.70GHz | 32.0 GB | local solve | 24 h 59 min |
| Workstation - Fujitsu Celsius R970 | 20 | Intel Xeon Gold 6148 @ 2.40GHz | 192 GB | local solve | 5 h 48 min |
| Rescale - Luna | 24 | 2nd Gen. Intel Xeon @ 3.0 GHz | 96 GB | 4 h 35 min | 4 h 44 min |
| Rescale - Emerald | 36 | Intel Xeon Platinum P-8124 @ 3.0 GHz | 144 GB | 3 h 26 min | 3h 37 min |
| Rescale - Hematite | 64 | AMD EPYC 7V73X @ 2.2 GHz | 448 GB | 1 h 27 min | 1 h 41 min |
| Rescale - Amber V2 | 120 | AMD EPYC 7742 @ 2.5 GHz | 480 GB | 1 h 37 min | 1h 51 min |
| Rescale - Rozenite | 120 | AMD EPYC 7V73X @ 2.2 GHz | 448 GB | 1 h 15 min | 1h 29 min |
The usual cost for Rescale hardware was about $14 with priority prices. The cheapest option was only 53 % of the most expensive. Hematite was the least expensive coretype. The running time difference between Hematite and the coretypes with a large number of cores was not significant.
18.3 million cells
| Core Count | Processor | System memory | Run time | Total time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workstation - Fujitsu Celsius R970 | 20 | Intel Xeon Gold 6148 @ 2.40GHz | 192 GB | local solve | 13 h 59 min |
| Rescale - Hematite | 64 | AMD EPYC 7V73X @ 2.2 GHz | 448 GB | 3h 32 min | 3h 55 min |
| Rescale - Amber V2 | 120 | AMD EPYC 7742 @ 2.5 GHz | 480 GB | 3h 36 min | 4h 2 min |
| Rescale - Rozenite | 120 | AMD EPYC 7V73X @ 2.2 GHz | 448 GB | 3h 3 min | 3h 27 min |
In the scenario with 18.3 million cells, the average cost was $25. Hematite continued to be the most budget-friendly coretype. The Hematite CPU is a bit newer than the one in the Amber V2 and the test case includes the multiphase model, likely impacting scalability negatively. As a result, it appears that the limit for efficient solution time is around 64 cores per node, and adding more cores beyond this point does not seem to decrease the solution time significantly.
Reflection
Using Rescale delivers significant advantages. Even with similar core counts the Rescale run outpaced the performance of the local Workstation. This is attributed to Rescale’s provision of the latest technology hardware components, while on-premise hardware tends to become outdated. The impact of using newer technology on simulation times can also be observed within Rescale. For instance, the CPU used in the Amber V2 was launched in 2019, while the CPU in the Hematite, launched in 2021, represents more recent technology.
The up-front costs of the tested workstations are 2500 € and 8000 €, but these number do not consider the additional costs for maintenance and upkeep. Furthermore, on-premise hardware leads to employee downtime while awaiting results. The cost of employees’ work hours is considerably higher than the hardware cost on Rescale.
During simulation runs on workstations, engaging in other activities is either impossible or very slow. Cloud computing, on the other hand, frees up the simulation engineer’s personal workstation for additional tasks, such as pre- or post-processing for another case. However, monitoring the job that is running in Rescale is straightforward in real-time.
In our test case, finding time to execute benchmark tests on local workstations was challenging. Particularly, simulations with six cores that took more than one night to solve had to be scheduled for weekends. This delay wouldn’t work for real-life situations needing quick results Rescale enable faster simulations and handles multiple simulations at once when necessary.
The 18.3 million cells simulation couldn’t have been possible on the 6-core laptop. The laptop’s memory was insufficient even for efficient mesh creation. However, on the 20-core workstation, meshing and case setup were seamless. Sending the job to Rescale was also straightforward. Using Rescale’s cloud computing opens up new possibilities to simulate processes that were impossible before due to hardware limits.